Creating a sketched video using OpenCV & Python
- Andrew Jones
- Oct 18, 2019
- 1 min read
A very quick post, showing how to take a video and create a 'sketched' version of it using OpenCV.
I have used and modified code that was originally posted here, so credit to askaswiss.com.
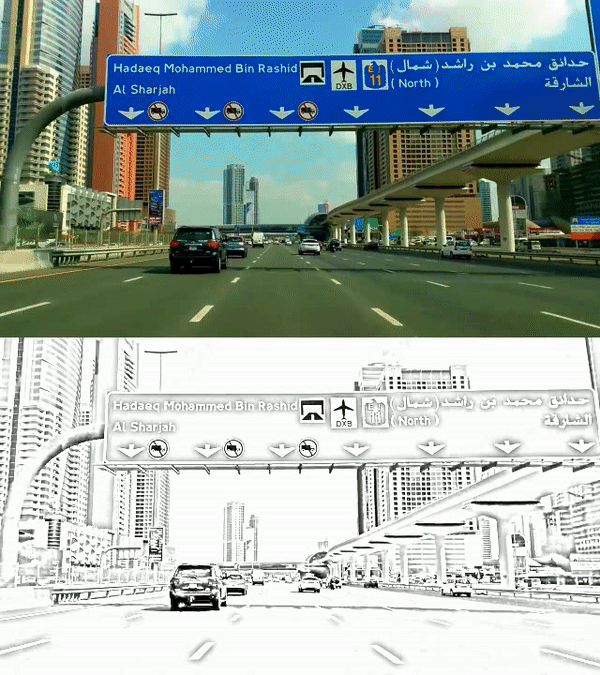
I've taken their code and applied it to a video file, stacking the output so we can see how cool the sketch looks vs. the original!
Code below:
#################################################################
# import packages
#################################################################
import numpy as np
import cv2
#################################################################
# bring in video file
#################################################################
cap = cv2.VideoCapture("driving_dubai_clipped.mp4")
#################################################################
# loop through frames
#################################################################
while True:
ret, frame = cap.read()
# convert to sketch
img_gray = cv2.cvtColor(frame, cv2.COLOR_RGB2GRAY)
img_blur = cv2.GaussianBlur(img_gray, (21, 21), 0, 0)
img_blend = cv2.divide(img_gray, img_blur, scale=256)
img_blend = cv2.cvtColor(img_blend,cv2.COLOR_GRAY2BGR)
# stack original and sketch frames
dual_image = np.vstack((img_blend,frame))
# display the resulting frame
cv2.imshow('img_contour',dual_image)
if cv2.waitKey(1) & 0xFF == ord('q'):
break
# release capture
cap.release()
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
We only require numpy and cv2 for this project.
After importing the video file, we loop through the frames, firstly converting to greyscale then applying a Gaussian blur to reduce noise in the frame. We then blend the original greyscale frame and the blurred frame, and I force it back to 3 colour channels using cv2.COLOR_GRAY2BGR purely so I can stack it with the original colour frame.
We then use numpy's vstack function to put the frames together and then visualise them. The result is below...